自定义算子
ONNX Runtime 提供了运行非官方 ONNX 算子的自定义算子选项。请注意,自定义算子与 贡献算子 不同,后者是直接内置到 ORT 中的选定非官方 ONNX 算子。
目录
定义和注册自定义算子
自 onnxruntime 1.16 起,自定义算子可以简单地实现为函数
void KernelOne(const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& X,
const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Y,
Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Z) {
auto input_shape = X.Shape();
auto x_raw = X.Data();
auto y_raw = Y.Data();
auto z_raw = Z.Allocate(input_shape);
for (int64_t i = 0; i < Z.NumberOfElement(); ++i) {
z_raw[i] = x_raw[i] + y_raw[i];
}
}
int main() {
Ort::CustomOpDomain v1_domain{"v1"};
// please make sure that custom_op_one has the same lifetime as the consuming session
std::unique_ptr<OrtLiteCustomOp> custom_op_one{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp("CustomOpOne", "CPUExecutionProvider", KernelOne)};
v1_domain.Add(custom_op_one.get());
Ort::SessionOptions session_options;
session_options.Add(v1_domain);
// create a session with the session_options ...
}
对于带有属性的自定义算子,也支持结构体:
struct Merge {
Merge(const OrtApi* ort_api, const OrtKernelInfo* info) {
int64_t reverse;
ORT_ENFORCE(ort_api->KernelInfoGetAttribute_int64(info, "reverse", &reverse) == nullptr);
reverse_ = reverse != 0;
}
// a "Compute" member function is required to be present
void Compute(const Ort::Custom::Tensor<std::string_view>& strings_in,
std::string_view string_in,
Ort::Custom::Tensor<std::string>* strings_out) {
std::vector<std::string> string_pool;
for (const auto& s : strings_in.Data()) {
string_pool.emplace_back(s.data(), s.size());
}
string_pool.emplace_back(string_in.data(), string_in.size());
if (reverse_) {
for (auto& str : string_pool) {
std::reverse(str.begin(), str.end());
}
std::reverse(string_pool.begin(), string_pool.end());
}
strings_out->SetStringOutput(string_pool, {static_cast<int64_t>(string_pool.size())});
}
bool reverse_ = false;
};
int main() {
Ort::CustomOpDomain v2_domain{"v2"};
// please make sure that mrg_op_ptr has the same lifetime as the consuming session
std::unique_ptr<Ort::Custom::OrtLiteCustomOp> mrg_op_ptr{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp<Merge>("Merge", "CPUExecutionProvider")};
v2_domain.Add(mrg_op_ptr.get());
Ort::SessionOptions session_options;
session_options.Add(v2_domain);
// create a session with the session_options ...
}
结构体需要一个 “Compute” 成员函数才能作为自定义算子运行。
对于这两种情况
- 输入需要声明为 const 引用。
- 输出需要声明为非 const 引用。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::Shape() 返回输入形状。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::Data() 返回原始输入数据。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::NumberOfElement() 返回输入中的元素数量。
- Ort::Custom::Tensor::Allocate(…) 分配一个输出并返回原始数据地址。
- 支持的模板参数有:int8_t, int16_t, int32_t, int64_t, float, double。
- 支持 std::string_view 作为输入和 std::string 作为输出,请在 此处 查找用法。
- 对于在 CPUExecutionProvider 上运行的自定义算子函数,支持 span 和 scalar 作为输入,请在 此处 查找用法。
- 对于需要内核上下文的自定义算子函数,请在 此处 查看示例。
- 当使用 unique_ptr 托管创建的自定义算子时,请务必使其与消费会话保持活跃。
自定义算子开发和注册的旧方式
开发自定义算子的旧方式仍然受支持,请参考 此处 的示例。
创建自定义算子库
自定义算子可以在单独的共享库中定义(例如,Windows 上的 .dll 或 Linux 上的 .so)。自定义算子库必须导出并实现 RegisterCustomOps 函数。RegisterCustomOps 函数将包含库自定义算子的 Ort::CustomOpDomain 添加到提供的会话选项中。请参考 此处 的项目和 此处 相关的 cmake 命令。
从自定义算子调用原生算子
为了简化自定义算子的实现,可以直接调用原生 onnxruntime 算子。例如,某些自定义算子可能需要在其他计算之间执行 GEMM 或 TopK。这对于节点(如 Conv)的预处理和后处理也很有用,例如用于状态管理目的。为此,Conv 节点可以被自定义算子(如 CustomConv)包装,在其中可以缓存和处理输入和输出。
此功能从 ONNX Runtime 1.12.0+ 开始支持。参见:API 和 示例。
用于 CUDA 和 ROCM 的自定义算子
自 onnxruntime 1.16 起,支持用于 CUDA 和 ROCM 设备的自定义算子。设备相关资源可以通过设备相关上下文直接从算子内部访问。以 CUDA 为例
void KernelOne(const Ort::Custom::CudaContext& cuda_ctx,
const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& X,
const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Y,
Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Z) {
auto input_shape = X.Shape();
CUSTOM_ENFORCE(cuda_ctx.cuda_stream, "failed to fetch cuda stream");
CUSTOM_ENFORCE(cuda_ctx.cudnn_handle, "failed to fetch cudnn handle");
CUSTOM_ENFORCE(cuda_ctx.cublas_handle, "failed to fetch cublas handle");
auto z_raw = Z.Allocate(input_shape);
cuda_add(Z.NumberOfElement(), z_raw, X.Data(), Y.Data(), cuda_ctx.cuda_stream); // launch a kernel inside
}
完整示例可在 此处 找到。为进一步方便开发,通过 CudaContext 公开各种 cuda ep 资源和配置,详情请参考 头文件。
对于 ROCM,它是这样的
void KernelOne(const Ort::Custom::RocmContext& rocm_ctx,
const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& X,
const Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Y,
Ort::Custom::Tensor<float>& Z) {
auto input_shape = X.Shape();
CUSTOM_ENFORCE(rocm_ctx.hip_stream, "failed to fetch hip stream");
CUSTOM_ENFORCE(rocm_ctx.miopen_handle, "failed to fetch miopen handle");
CUSTOM_ENFORCE(rocm_ctx.rblas_handle, "failed to fetch rocblas handle");
auto z_raw = Z.Allocate(input_shape);
rocm_add(Z.NumberOfElement(), z_raw, X.Data(), Y.Data(), rocm_ctx.hip_stream); // launch a kernel inside
}
详细信息可在 此处 找到。
一个算子,多种类型
自 onnxruntime 1.16 起,自定义算子允许支持多种数据类型
template <typename T>
void MulTop(const Ort::Custom::Span<T>& in, Ort::Custom::Tensor<T>& out) {
out.Allocate({1})[0] = in[0] * in[1];
}
int main() {
std::unique_ptr<OrtLiteCustomOp> c_MulTopOpFloat{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp("MulTop", "CPUExecutionProvider", MulTop<float>)};
std::unique_ptr<OrtLiteCustomOp> c_MulTopOpInt32{Ort::Custom::CreateLiteCustomOp("MulTop", "CPUExecutionProvider", MulTop<int32_t>)};
// create a domain adding both c_MulTopOpFloat and c_MulTopOpInt32
}
在自定义算子中封装外部推理运行时
自定义算子可以封装整个模型,然后通过外部 API 或运行时进行推理。这有助于将外部推理引擎或 API 与 ONNX Runtime 集成。
例如,考虑以下 ONNX 模型,其中包含一个名为“OpenVINO_Wrapper”的自定义算子。“OpenVINO_Wrapper”节点以 OpenVINO 的原生模型格式(XML 和 BIN 数据)封装了一个完整的 MNIST 模型。模型数据被序列化到节点的属性中,然后由自定义算子的内核检索,以构建模型的内存表示并使用 OpenVINO C++ API 运行推理。
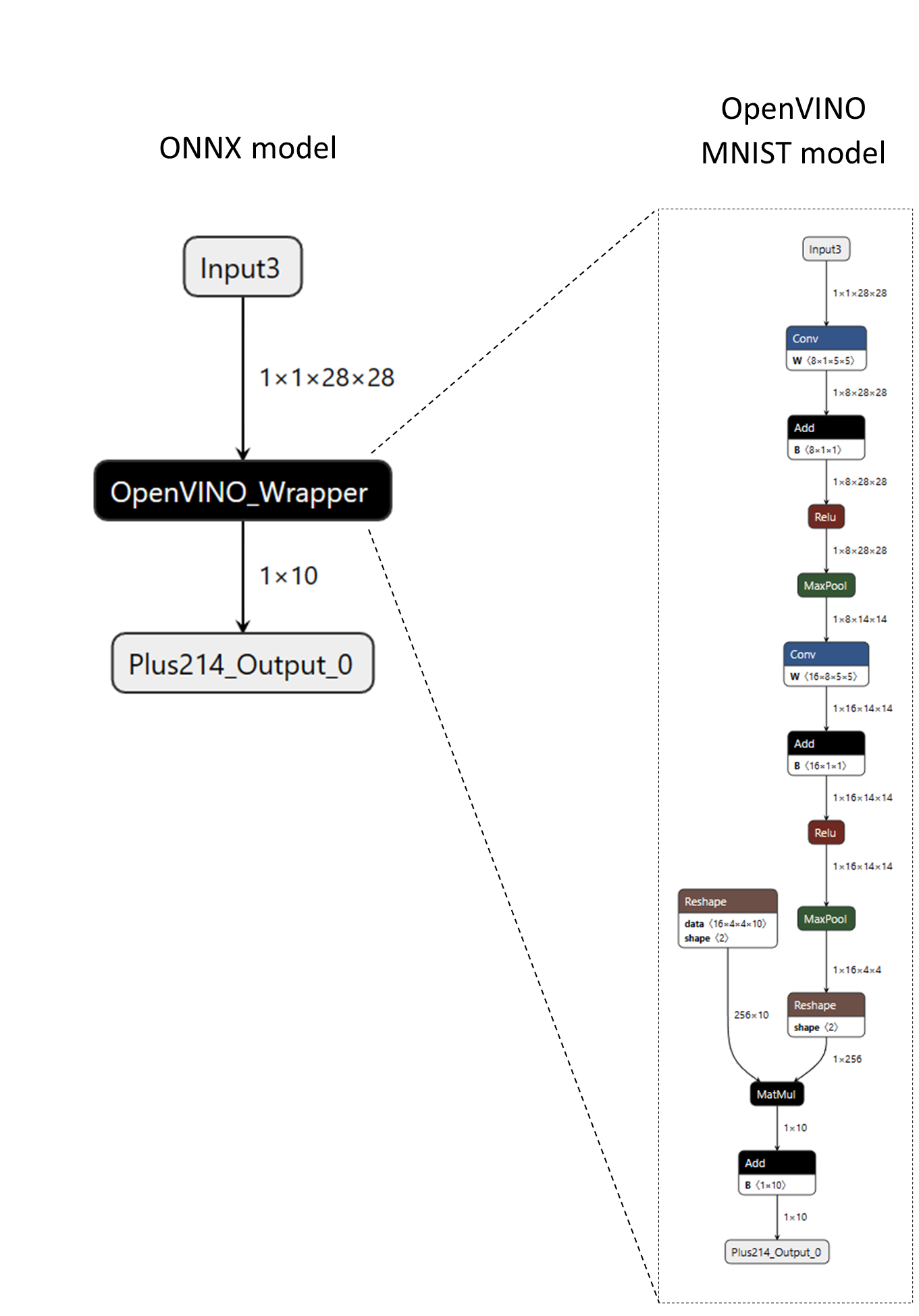
以下代码片段展示了如何定义自定义算子。
// Note - below code utilizes legacy custom op interfaces
struct CustomOpOpenVINO : Ort::CustomOpBase<CustomOpOpenVINO, KernelOpenVINO> {
explicit CustomOpOpenVINO(Ort::ConstSessionOptions session_options);
CustomOpOpenVINO(const CustomOpOpenVINO&) = delete;
CustomOpOpenVINO& operator=(const CustomOpOpenVINO&) = delete;
void* CreateKernel(const OrtApi& api, const OrtKernelInfo* info) const;
constexpr const char* GetName() const noexcept {
return "OpenVINO_Wrapper";
}
constexpr const char* GetExecutionProviderType() const noexcept {
return "CPUExecutionProvider";
}
// IMPORTANT: In order to wrap a generic runtime-specific model, the custom operator
// must have a single non-homogeneous variadic input and output.
constexpr size_t GetInputTypeCount() const noexcept {
return 1;
}
constexpr size_t GetOutputTypeCount() const noexcept {
return 1;
}
constexpr ONNXTensorElementDataType GetInputType(size_t /* index */) const noexcept {
return ONNX_TENSOR_ELEMENT_DATA_TYPE_UNDEFINED;
}
constexpr ONNXTensorElementDataType GetOutputType(size_t /* index */) const noexcept {
return ONNX_TENSOR_ELEMENT_DATA_TYPE_UNDEFINED;
}
constexpr OrtCustomOpInputOutputCharacteristic GetInputCharacteristic(size_t /* index */) const noexcept {
return INPUT_OUTPUT_VARIADIC;
}
constexpr OrtCustomOpInputOutputCharacteristic GetOutputCharacteristic(size_t /* index */) const noexcept {
return INPUT_OUTPUT_VARIADIC;
}
constexpr bool GetVariadicInputHomogeneity() const noexcept {
return false; // heterogenous
}
constexpr bool GetVariadicOutputHomogeneity() const noexcept {
return false; // heterogeneous
}
// The "device_type" is configurable at the session level.
std::vector<std::string> GetSessionConfigKeys() const { return {"device_type"}; }
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> session_configs_;
};
请注意,自定义算子被定义为具有单个变长/异构输入和单个变长/异构输出。这是为了能够封装具有不同输入和输出类型和形状的 OpenVINO 模型(而不仅仅是 MNIST 模型)。有关输入和输出特征的更多信息,请参阅 OrtCustomOp 结构体文档。
此外,自定义算子声明“device_type”为一个会话配置,可由应用程序设置。以下代码片段展示了如何注册和配置包含上述自定义算子的自定义算子库。
Ort::Env env;
Ort::SessionOptions session_options;
Ort::CustomOpConfigs custom_op_configs;
// Create local session config entries for the custom op.
custom_op_configs.AddConfig("OpenVINO_Wrapper", "device_type", "CPU");
// Register custom op library and pass in the custom op configs (optional).
session_options.RegisterCustomOpsLibrary("MyOpenVINOWrapper_Lib.so", custom_op_configs);
Ort::Session session(env, ORT_TSTR("custom_op_mnist_ov_wrapper.onnx"), session_options);
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 完整的 OpenVINO 自定义算子封装示例。要创建封装外部模型或权重的 ONNX 模型,请参阅 create_custom_op_wrapper.py 工具。